At the heart of this ancient practice of yoga lies the seven classifications of asanas, or yoga poses, each distinct in its purpose and impact. From the dynamic flow of moving sequences to the grounding strength of standing poses, the graceful poise of balancing poses, the heart-opening backbends, the introspective forward bends, the detoxifying twists, and the empowering inversions, these categories form the foundational pillars of yoga practice. Join me as we delve into the essence of each classification, exploring their benefits, techniques, and the profound transformation they can bring to our bodies and minds.
Benefits of Practicing Yoga Asanas
Yoga asanas offer a plethora of benefits that go beyond physical fitness. While the poses help strengthen and tone our muscles, improve flexibility, and enhance body awareness, their impact reaches deeper levels. Regular practice of yoga asanas brings about a sense of mental clarity, emotional stability, and spiritual connection. The combination of physical movement, breath control, and mindfulness cultivates a unique balance and harmony within ourselves, leaving us feeling rejuvenated and centered.
One key benefit of practicing yoga asanas is stress reduction. As we move through the poses, focusing on our breath and body, we release tension and quiet the mind. This leads to a decrease in stress hormones, such as cortisol, and an increase in feel-good hormones, such as endorphins. Practicing yoga asanas also improves our overall well-being by promoting better sleep, boosting immune function, and increasing energy levels.
In addition to the physical and mental benefits, practicing yoga asanas also provides an opportunity for profound self-reflection and personal growth. Through the challenges and triumphs of practicing the poses, we learn valuable lessons about patience, perseverance, and self-acceptance. The journey of yoga is not just about achieving the perfect pose but about embracing the process and discovering our inner strength, empowering us to grow and evolve.
Understanding the 7 Types of Asanas in Yoga
To fully appreciate the depth and diversity of yoga asanas, it is crucial to understand the seven types or classifications they fall into. Each category represents a different aspect of the practice and offers its unique benefits. Let’s delve into each type, equipping ourselves with the knowledge to enhance our yoga practice.
Category 1: Moving Sequences
Moving sequences in yoga, also known as vinyasa or flow, involve linking poses together in a continuous and fluid manner. This dynamic style of practice builds strength, flexibility, and cardiovascular endurance. Moving sequences can be fast-paced or slow and mindful, depending on the individual’s preference and level of experience. The transitions between poses are as important as the poses themselves, as they encourage a seamless flow of movement and breath. This type of asana practice promotes a sense of meditation in motion, allowing practitioners to cultivate focus and presence on the mat.
A popular example of a moving sequence is the Sun Salutation, a series of poses performed in a specific order. This sequence warms up the body, stretches the muscles, and prepares the practitioner for a deeper practice. You can also tailor your moving sequences to specific intentions, such as energizing sequences to start the day or relaxing sequences to wind down in the evening.
Category 2: Standing Asanas
Standing asanas form the foundation of yoga, providing stability, strength, and grounding. We often hold these poses longer, allowing practitioners to cultivate a deep connection with the earth beneath them. Standing asanas improve balance, posture, and concentration. They also strengthen the legs, core, and back muscles, promoting overall stability and spinal alignment.
Some common standing asanas include Tadasana (Mountain Pose), Virabhadrasana II (Warrior II), and Trikonasana (Triangle Pose). These poses require a strong foundation and mindful engagement of the entire body, from the feet to the fingertips. Standing asanas not only build physical strength but also instill a sense of confidence and poise.
Psssst! Are you looking to learn more about alignment? Transform your life with the world’s leading yoga teacher training in Bali or Costa Rica. We create highly curated, life-changing yoga and meditation trainings with master-level instructors from India and the West. Whether new to yoga or seeking to deepen your practice, our training caters to all levels, ensuring the best yoga teacher training experience possible.
Category 3: Balancing Asanas
Balancing asanas challenge our stability and focus, both physically and mentally. These poses require a combination of strength, flexibility, and concentration. Balancing asanas improve coordination, proprioception (awareness of body position in space), and mental clarity. They also help strengthen the core, legs, and ankle muscles.
Examples of balancing asanas include Vrksasana (Tree Pose), Bakasana (Crow Pose), and Natarajasana (Dancer’s Pose). These poses often involve standing on one leg or finding equilibrium in challenging positions. Balancing asanas teach us to find steadiness amidst movement and chaos, both on and off the mat.
Category 4: Backbending Asanas
Backbending asanas open up the front of the body, stretching the chest, shoulders, and hip flexors. These poses counteract the effects of prolonged sitting and hunching forward, which can lead to poor posture and tightness in the chest and shoulders. Backbending asanas promote spinal flexibility, increase lung capacity, and stimulate the nervous system. They also help to cultivate courage, vulnerability, and a sense of expansion.
Popular back-bending asanas include Ustrasana (Camel Pose), Urdhva Dhanurasana (Upward Bow Pose), and Setu Bandha Sarvangasana (Bridge Pose). These poses require a combination of strength, flexibility, and an openness to vulnerability. Backbending asanas invite us to embrace the unknown and trust in our innate resilience.

Category 5: Forward Bending Asanas
Forward-bending asanas bring a sense of introspection and surrender to our practice. These poses gently stretch the muscles of the back body, including the hamstrings, calves, and lower back. Forward-bending asanas promote relaxation, release tension in the spine, and stimulate the digestive system. They also calm the mind and nervous system, making them ideal for stress relief and winding down before sleep.
Well-known forward-bending asanas include Paschimottanasana (Seated Forward Bend), Uttanasana (Standing Forward Bend), and Balasana (Child’s Pose). These poses encourage us to turn our attention inward, let go of striving, and simply be present in the moment. Forward-bending asanas teach us the power of surrender and acceptance.
Category 6: Twisting Asanas
Twisting asanas detoxify and rejuvenate the body, improving digestion, spinal mobility, and overall vitality. These poses involve rotating the spine, which helps to wring out toxins and stagnant energy from the organs and tissues. Twisting asanas also tone the abdominal muscles, stimulate the lymphatic system, and enhance spinal flexibility. They offer a sense of cleansing and renewal, both physically and energetically.
Examples of twisting asanas include Bharadvajasana (Bharadvaja’s Twist), Marichyasana (Marichi’s Pose), and Ardha Matsyendrasana (Half Lord of the Fishes Pose). These poses require a combination of strength, flexibility, and mindful engagement of the breath. Twisting asanas encourage us to release what no longer serves us and make space for new possibilities.

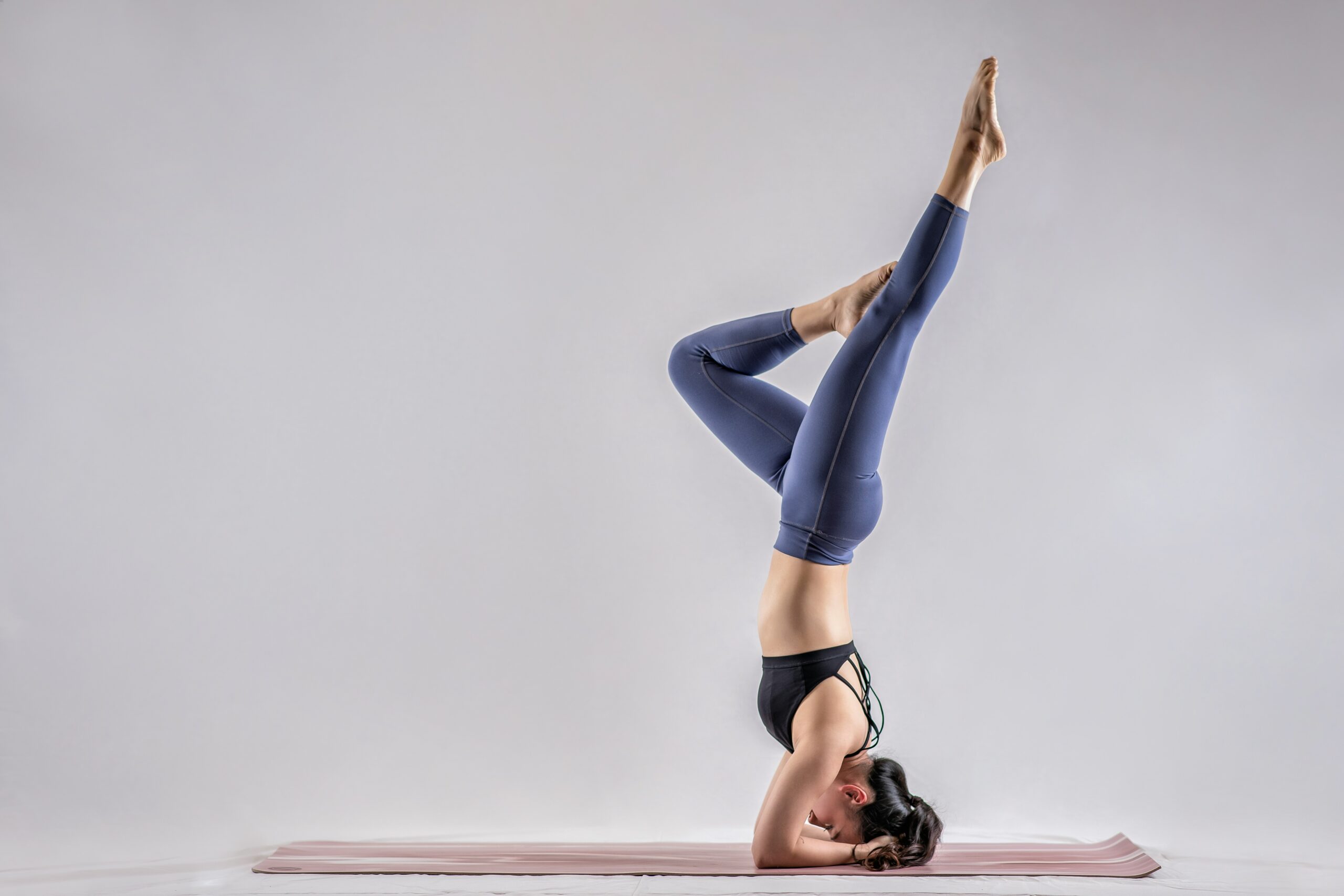
Category 7: Inversion Asanas
Inversion asanas turn our world upside down, quite literally. These poses involve taking the head below the heart, whether through shoulder stands, headstands, or handstands. Inversion asanas reverse the effects of gravity, benefiting the circulatory, lymphatic, and nervous systems. They also cultivate focus, balance, and inner strength. Inversions are often considered the “king” or “queen” of asanas, as they require physical and mental mastery.
Popular inversion asanas include Sirsasana (Headstand), Adho Mukha Vrksasana (Handstand), and Salamba Sarvangasana (Shoulderstand). These poses should be approached with caution and proper guidance, as they require strength, stability, and awareness. Inversion asanas teach us to see the world from a different perspective and embrace the unknown with courage.
The Power of Asanas in Yoga
The seven types of asanas in yoga offer a comprehensive approach to physical and mental well-being. From the dynamic flow of moving sequences to the grounding strength of standing poses, the graceful poise of balancing poses, the heart-opening backbends, the introspective forward bends, the detoxifying twists, and the empowering inversions, each category brings its own unique benefits and challenges. By incorporating a variety of asanas into our practice, we can cultivate balance, strength, flexibility, and inner harmony. So, step onto your mat and explore the vast world of yoga asanas, discovering their transformative power for your body, mind, and spirit.
Want to learn more?
Check out the East+West yoga teacher training in Bali or Costa Rica. We create highly curated, life-changing yoga and meditation trainings with master-level instructors from India and the West. Whether you’re new to yoga or seeking to deepen your practice, our training caters to all levels, ensuring the best yoga teacher training experience possible.